Transport of Gases
Transport of Gases: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Oxygen Dissociation Curve, Haldane Effect, Chloride Shift, Exchange of Gases, Carbonic Anhydrase, Transport of Oxygen, Carbamino-haemoglobin, Transport of Gases, Oxyhaemoglobin and, Transport of Carbon Dioxide
Important Questions on Transport of Gases
A large proportion of oxygen is left unused in the human blood even after its uptake by the body tissues. This O2
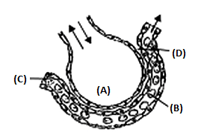
The figure given below shows a small part of human lung where exchange of gases takes place. In which one of the options given below, the one part A, B, C or D is correctly identified along with its function?
The majority of carbon dioxide produced by our body cells is transported to the lungs
Which one of the following statements about blood constituents and transport of respiratory gases is most accurate?
The carbon dioxide is transported via blood to lungs as:
Although much CO2 is carried in blood, bloods does not become acidic because
Oxygen dissociation curve of haemoglobin is
Carbon dioxide is transported from tissue to respiratory surface by only
Blood analysis of a patient reveals an unusually high quantity of carboxyhaemoglobin content. Which of the following conclusions is most likely to be correct?
"The patient has been inhaling polluted air containing unusually high content of ___________________."
Which one of the following organs in the human body is most affected due to shortage of oxygen?
The process of migration of chloride ions from the plasma to RBC and that of carbonate ions from RBC to plasma is
The exchange of gases in the alveoli of the lungs takes place during respiration. Identify the labeling a-e.
In alveoli of the lungs, the air at the site of gas exchange, is separated from the blood by
Which among the given ones is the most probable reason for higher diffusion rate of CO2 than O2 through diffusion membrane, for per unit difference in partial pressure?
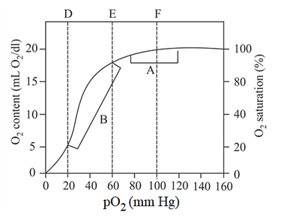
Which of these is correct regarding , and areas in the graph?
Study the following statements
I. Effect of CO2 and H+ on the oxygen affinity of haemoglobin is termed Bohr effect.
II. Formation of carbonic acid is faster in plasma than RBC due to the carbonic anhydrase.
III. Decrease in pH, increase in CO2 and temperature shifts oxyhaemoglobin dissociation curve to the left side.
IV. Exchange of chloride and bicarbonate ions between RBC and plasma is called Hamburger's phenomenon.
Correct statements are:
Blood transport of occurs in three forms. The correct percentages of in these forms are
| As Carbaminohaemoglobin in RBC |
As Bicarbonates |
Dissolved Form in Plasma |
| a. | ||
| b. | ||
| c. | ||
| d. |
Which of the following is not true?